Fibroids :
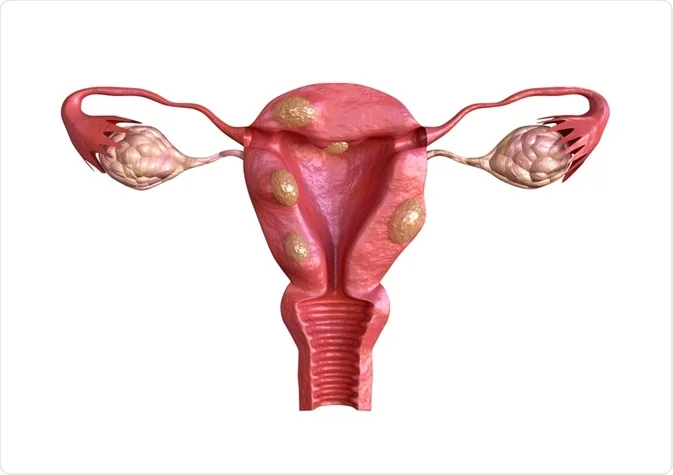
Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths that develop in or around the uterus, commonly affecting women during their reproductive years. Their exact cause is unknown, but hormones and genetic factors play a key role. Many women have fibroids without symptoms, while others may experience significant discomfort.
Fibroids can range in size from very small (undetectable) to large masses that may enlarge or distort the uterus. A woman may have a single fibroid or multiple fibroids, and in rare cases, they can grow large enough to reach the rib cage.
Symptoms of Fibroids
Many women do not experience symptoms. When present, symptoms depend on the size, number, and location of fibroids and may include:
Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding
Periods lasting longer than one week
Pelvic pressure or pain
Frequent urination or difficulty emptying the bladder
Constipation
Lower back or leg pain
Risk Factors
Factors that may increase the risk of developing fibroids include:
Family history (mother or sister with fibroids)
Early onset of menstruation
Obesity
Vitamin D deficiency
Diet high in red meat and low in fruits, vegetables, and dairy
Alcohol consumption
Causes
Although the exact cause is unclear, fibroid growth is linked to:
Hormonal influence: Estrogen and progesterone promote fibroid growth
Genetic changes: Many fibroids contain altered genes
Growth factors: Substances like insulin-like growth factor may contribute
Extracellular matrix (ECM): Increased ECM makes fibroids firm and fibrous
Fibroids often shrink after menopause due to reduced hormone levels.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on symptoms, fibroid size, and future fertility plans. Options include:
Medications to manage symptoms
Minimally invasive procedures
Surgical removal of fibroids or the uterus, when necessary
Early evaluation helps in choosing the most effective and least invasive treatment.
